In recent years, the healthcare industry has witnessed an unprecedented surge in technological advancements, transforming the way medical professionals diagnose, treat, and manage various health conditions. This article delves into the remarkable innovations that are reshaping healthcare, blending cutting-edge technology with traditional medical practices.
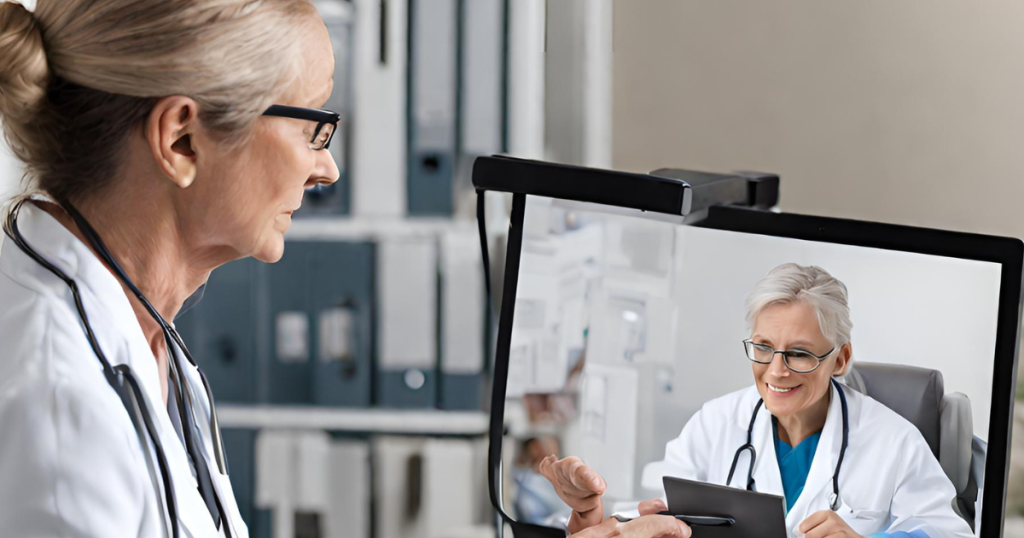

Telemedicine and Remote Patient Monitoring:
The advent of telemedicine has ushered in a new era of healthcare accessibility. Now, patients can connect with healthcare professionals from the comfort of their homes, eliminating geographical barriers. Remote patient monitoring devices allow real-time tracking of vital signs, enabling physicians to provide personalized care plans and intervene promptly in case of any anomalies.
Artificial Intelligence in Diagnostics:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a game-changer in diagnostic processes. Machine learning algorithms analyze vast amounts of medical data to detect patterns and anomalies, assisting healthcare professionals in making more accurate and timely diagnoses. This not only enhances efficiency but also contributes to early detection and treatment.
3D Printing in Healthcare:
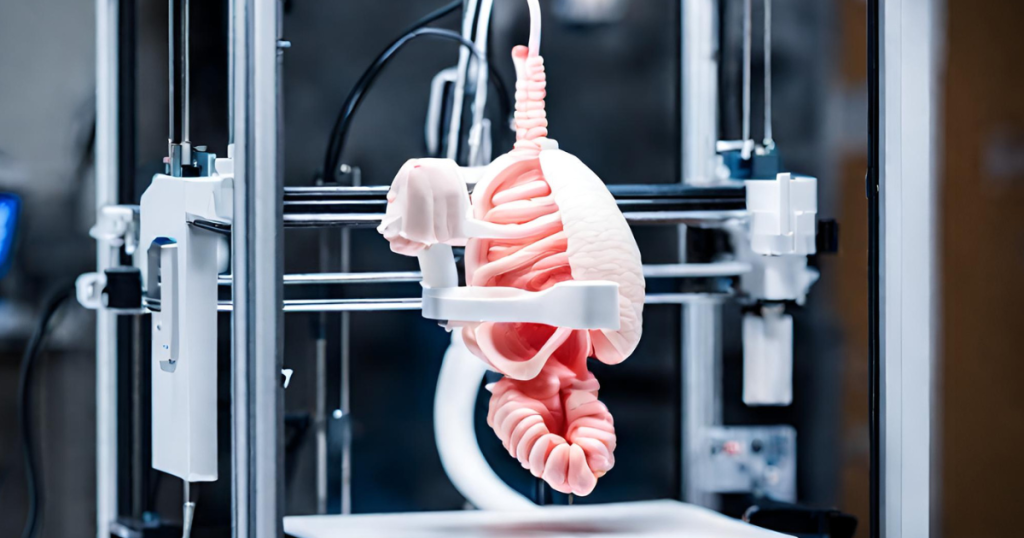
The integration of 3D printing technology has revolutionized medical procedures, particularly in surgical planning and the creation of customized implants. Surgeons can now practice complex surgeries on 3D-printed models of patients’ organs, leading to improved precision and reduced risks during actual procedures. Additionally, patient-specific implants are designed for better compatibility and effectiveness.
Robotics in Surgery:
Robotic-assisted surgeries have become increasingly prevalent, offering enhanced precision and control. Surgeons can now perform minimally invasive procedures with the help of robotic systems, leading to shorter recovery times and reduced postoperative complications. The marriage of human expertise and robotic precision is pushing the boundaries of what is achievable in the operating room.
Blockchain for Health Records:
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing the management of electronic health records. With its secure and decentralized nature, blockchain ensures the integrity and privacy of patient data. This innovation not only streamlines data sharing among healthcare providers but also empowers patients with greater control over their health information.
Precision Medicine:
The era of one-size-fits-all treatments is fading away, thanks to the rise of precision medicine. This approach tailors medical interventions to individual patients based on their genetic makeup, lifestyle, and environmental factors. By personalizing treatment plans, healthcare providers can achieve higher success rates and minimize adverse effects.
Nanotechnology in Healthcare:
Nanotechnology is making waves in drug delivery and diagnostics. Nano-sized particles enable targeted drug delivery, minimizing side effects and improving the efficacy of treatments. Additionally, nanosensors provide real-time monitoring of biomarkers, facilitating early detection of diseases.
Virtual Reality (VR) in Rehabilitation:
Virtual Reality is finding its place in healthcare, particularly in rehabilitation therapies. Patients recovering from injuries or surgeries can engage in immersive VR experiences that simulate real-world scenarios. This not only makes the rehabilitation process more engaging but also aids in the restoration of motor skills and cognitive functions.
Wearable Health Technology:
The rise of wearable devices, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, has empowered individuals to take control of their health. These devices monitor various health metrics, including heart rate, activity levels, and sleep patterns. The collected data provides users with insights into their well-being, promoting preventive healthcare and early intervention
Gene Editing and CRISPR Technology:
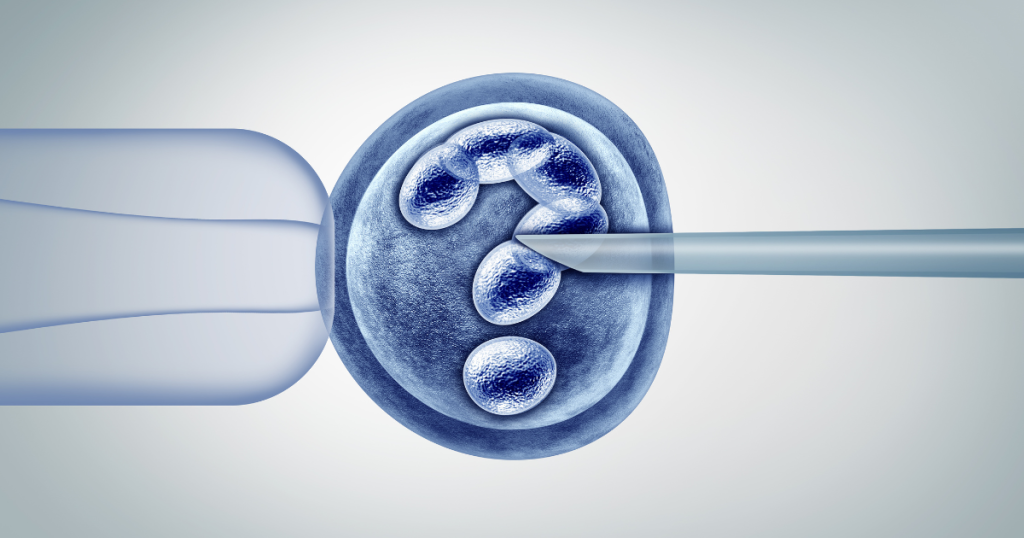
The field of genetics has seen groundbreaking advancements with the development of CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) technology. This revolutionary tool allows scientists to edit genes with unprecedented precision. While still in its early stages, CRISPR holds immense potential for treating genetic disorders and diseases at their root.
Smart Hospitals and IoT Integration:
The concept of smart hospitals involves the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices to enhance overall healthcare management. From connected medical devices to automated patient monitoring systems, smart hospitals streamline operations, reduce errors, and improve the overall patient experience.
Regenerative Medicine:
Regenerative medicine focuses on harnessing the body’s natural healing processes to repair or replace damaged tissues and organs. Stem cell therapy, tissue engineering, and other regenerative approaches hold promise for treating conditions that were once considered incurable, paving the way for transformative treatments in the future.
Cognitive Computing in Healthcare:
Cognitive computing systems, powered by artificial intelligence, are assisting healthcare professionals in analyzing vast amounts of clinical data. These systems can identify patterns, suggest treatment options, and even predict potential health risks. This aids in making more informed decisions and providing personalized care to patients.
Bioprinting and Organ Transplants:
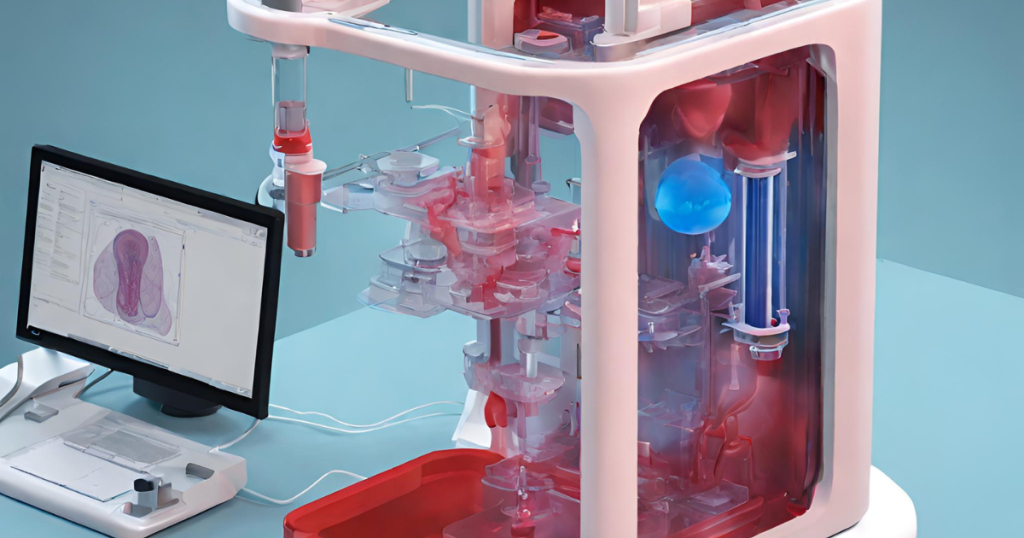
Bioprinting technology allows the creation of three-dimensional tissues and organs using a patient’s cells. This innovation has the potential to address the shortage of organ donors and reduce transplant rejection rates. While still in its infancy, bioprinting holds great promise for the future of organ transplantation.
Mind-Body Interventions for Mental Health:
The integration of mind-body interventions, such as mindfulness and meditation, into mainstream healthcare is gaining traction. These practices have shown positive effects on mental health, reducing stress, anxiety, and depression. Healthcare providers are increasingly incorporating these holistic approaches to complement traditional treatments.
Health Information Exchange (HIE):
Health Information Exchange facilitates the secure sharing of patient information across different healthcare providers. This interconnected system improves care coordination, reduces duplication of tests and procedures, and ensures that crucial medical information is readily available to authorized professionals, enhancing the overall efficiency of healthcare delivery.
Augmented Reality (AR) for Medical Training:
Augmented Reality is making waves in medical education by providing immersive, interactive experiences for training healthcare professionals. Surgeons, for instance, can use AR to visualize complex procedures in real-time, enhancing their skills and improving patient outcomes. This technology bridges the gap between theoretical knowledge and hands-on practice.
Nutrigenomics:
Nutrigenomics explores the relationship between an individual’s genetics and their response to different foods. By understanding how genetic factors influence dietary needs, healthcare providers can offer personalized nutrition plans. This tailored approach has the potential to optimize health and prevent lifestyle-related diseases.
Health Apps and Gamification:
Mobile health applications and gamification techniques are engaging individuals in their healthcare journey. These apps help users track their fitness, monitor chronic conditions, and even receive personalized health recommendations. The integration of gamification elements, such as rewards and challenges, encourages users to adopt healthier lifestyles.
Social Determinants of Health (SDOH):
Recognizing that health outcomes are influenced by social and economic factors, healthcare providers are increasingly addressing social determinants of health. This holistic approach considers elements like housing, education, and employment, aiming to eliminate disparities and create a more equitable healthcare system.
Biorobotics and Prosthetics:
Advancements in biorobotics have led to the development of more sophisticated prosthetic limbs. These devices, equipped with sensors and AI, can provide a more natural range of motion, improving the quality of life for amputees. Biorobotics also plays a role in developing exoskeletons for rehabilitation and support
Environmental Health Monitoring:
Monitoring environmental factors that impact health, such as air and water quality, is becoming increasingly important. Technology allows for real-time tracking and analysis, enabling communities and healthcare professionals to address environmental health issues promptly and prevent related health concerns.
Personalized Vaccines:
The concept of personalized vaccines tailors immunizations to an individual’s specific genetic makeup. This approach aims to enhance vaccine efficacy and reduce adverse reactions. As the understanding of immunogenetics grows, personalized vaccines could play a crucial role in preventing infectious diseases.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in Healthcare Administration:
Robotic Process Automation streamlines administrative tasks in healthcare, such as billing, scheduling, and data entry. By automating repetitive processes, RPA reduces errors, cuts down on operational costs, and allows healthcare professionals to focus more on patient care.
Blockchain for Drug Traceability:
Blockchain technology is being employed to enhance the traceability of pharmaceuticals. By creating an immutable and transparent ledger, blockchain ensures the authenticity of drugs throughout the supply chain. This not only reduces the risk of counterfeit medications but also improves drug safety and regulatory compliance.
Human Augmentation:

Human augmentation involves enhancing human capabilities through the integration of technology. In healthcare, this could include technologies like exoskeletons that assist with physical tasks, smart prosthetics controlled by neural signals, and brain-computer interfaces. These innovations have the potential to improve mobility and independence for individuals with physical disabilities.
Predictive Analytics for Epidemic Management:
Predictive analytics leverages historical data and machine learning algorithms to forecast disease outbreaks and epidemics. This proactive approach allows healthcare organizations and public health officials to allocate resources effectively, implement preventive measures, and mitigate the impact of infectious diseases on communities.
Federated Learning for Medical Research:
Federated learning enables collaborative model training across mulmtiple decentralized healthcare institutions without sharing raw patient data. This privacy-preserving approach facilitates medical research by aggregating knowledge from various sources, fostering advancements in disease understanding, treatment development, and healthcare outcomes.
Digital Therapeutics:
Digital therapeutics are evidence-based software applications designed to treat medical conditions. These interventions often work in conjunction with traditional treatments and can include mobile apps, virtual reality experiences, or interactive platforms. They offer scalable and cost-effective solutions for managing chronic diseases and mental health conditions.
Healthcare Chatbots and Virtual Health Assistants:
Chatbots and virtual health assistants leverage natural language processing and AI to provide immediate responses to user queries. These tools assist with appointment scheduling, medication reminders, and general health inquiries. They contribute to improved patient engagement, accessibility, and healthcare resource optimization.
Metaverse Integration in Medical Education:
The metaverse, a virtual shared space, is finding applications in medical education. Virtual simulations and 3D environments allow medical students to explore anatomy, practice procedures, and collaborate with peers globally. This immersive approach enhances the learning experience and bridges geographical gaps in medical training.
Conclusion:
The ever-expanding landscape of healthcare innovations showcases the incredible strides made in merging technology with medical practices. From blockchain ensuring drug safety to predictive analytics preparing for epidemics, these advancements are not only improving patient care but also transforming the very fabric of the healthcare ecosystem. As we look ahead, the continued synergy between healthcare and technology promises a future where healthcare is not just reactive but anticipatory, personalized, and accessible to all.
Recent Comments